Description
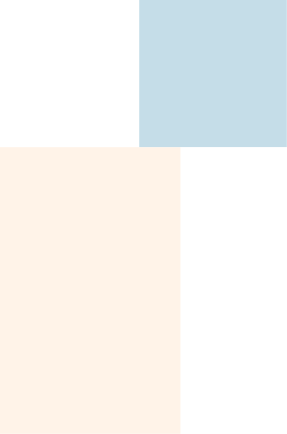
Seamless steel pipe is a tubular section or hollow cylinder, usually but not necessarily of circular cross-section, used mainly to convey substances that can flow — liquids and gases (fluids), slurries, powders and masses of small solids.
Seamless Pipe (and tubing) is made by extruding a steel block or by drilling a solid steel bar. Next, the extrusion or the drilled steel bar is cold drawn through a dye to achieve the diameter and thickness needed. Because this process can cause mechanical hardening, sometimes the material is annealed and straightened as a final process. Seamless Pipe & Tubing is subdivided as:
Cold Drawn Seamless, or CDS, exhibits precise tolerances and a good surface finish.
Hot Finished Seamless or HFS has less critical tolerances and a somewhat scaly finish and is not as strong as CDS.
For Drawn over Mandrel, or DOM tubing, the first stages of manufacturing are identical to the ones used to make electric resistance welded tubing, but in the finishing stages the entire flash weld is taken out and the tube is cold drawn over a mandrel. A mandrel is a round object against which material can be forged or shaped. The cold-drawn process provides the tube with better dimensional tolerances, improved surface finish and the strongest weld strength achievable.

ASTM A106 and A53 are two commonly used specifications for seamless carbon steel pipes. They are widely used in various industries such as oil and gas, construction, and mechanical engineering.
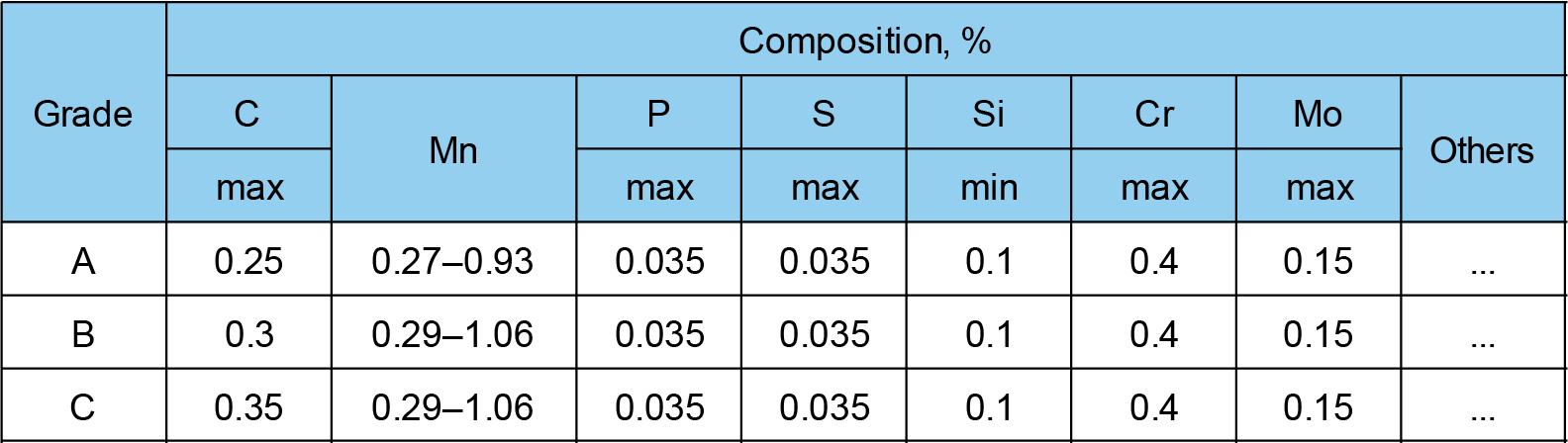
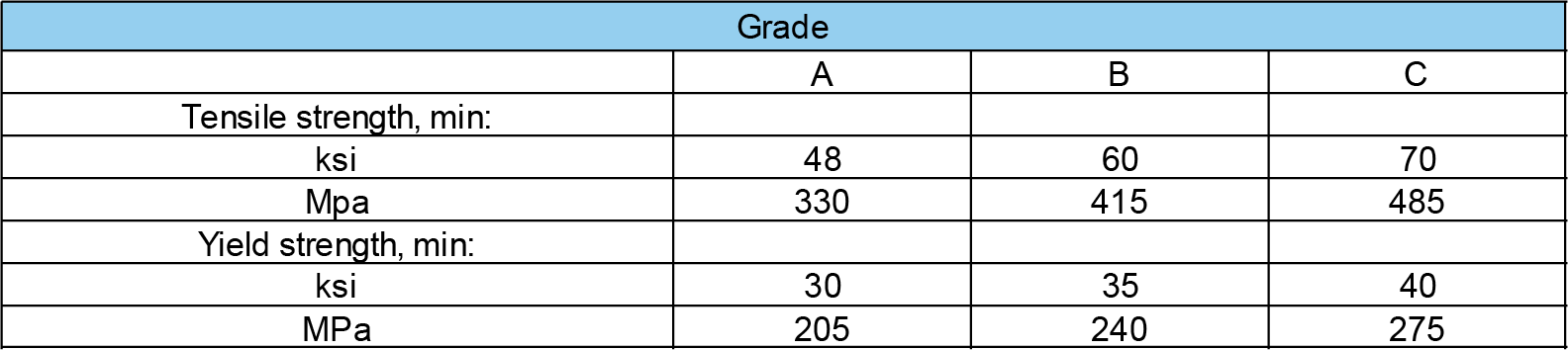
ASTM A106 covers seamless carbon steel pipes for high-temperature service (up to 750°F) and pressure applications. It includes grades A, B, and C, which are different in terms of their chemical composition and mechanical properties.
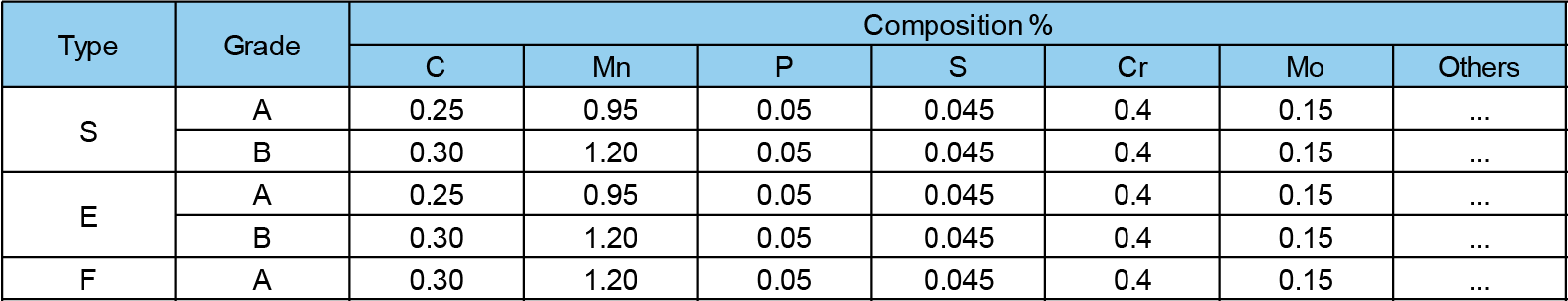
ASTM A53 covers seamless and welded black and hot-dipped galvanized steel pipes in NPS (National Pipe Size) 1/8 to NPS 26 (DN 6 to DN 650). The steel categorized in this standard must be open-hearth, basic-oxygen, or electric-furnace processed and must have the following chemical requirements: carbon, manganese, phosphorus, sulfur, copper, nickel, chromium, molybdenum, and vanadium. The types of steel for the pipe fittings include Grade A and Grade B.
Both standards specify different requirements for mechanical properties, chemical composition, and testing. It is important to select the appropriate specification based on the specific application and requirements.
ASTM A106: American Society for Testing and Materials
Seamless Carbon Steel Pipe for High-Temperature Service
Application: Oil, Gas and water delivery; Refinery, Boiler and Mechanical equipment manufacturer; structure construction; drilling, ship building and etc.
ASTM A53: American Society for Testing and Materials
Steel, Black and Hot-Dipped, Zinc-Coated, Welded and Seamless
Application: Oil, Gas and water delivery; Refinery, Boiler and Mechanical equipment manufacturer; structure construction; drilling, ship building and etc.
ASTM A106 Chemical Requirements
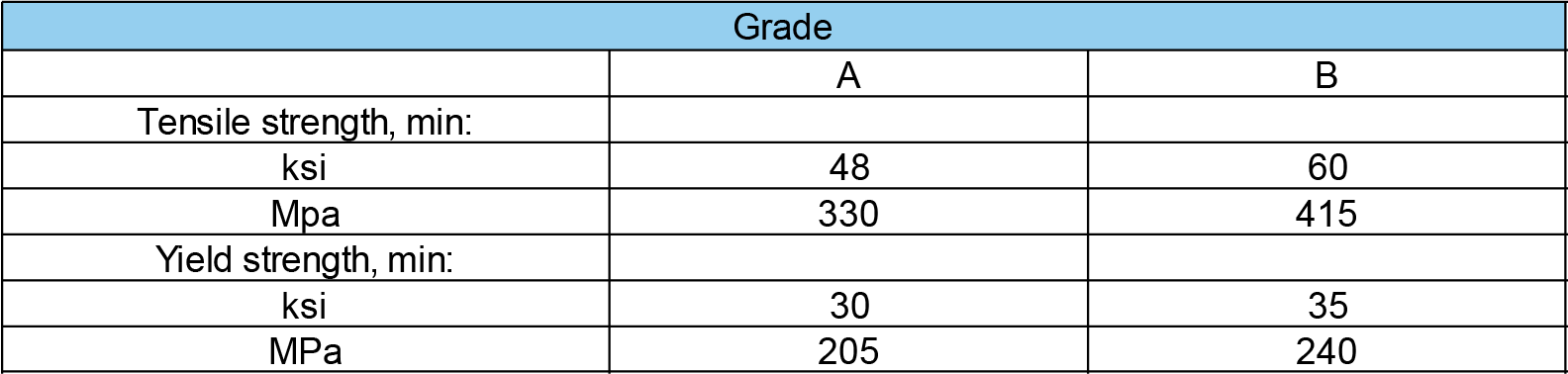
Mechanical Properties
ASTM A53 Chemical Requirements
Mechanical Properties
Rich production technology, advanced equipment, high automation degree and high production precision, complete molding. As the designated supplier of major energy enterprise groups under the jurisdiction of SASAC, the company has won a number of national and provincial reputations.









